|
We linked a two dimensional coastal upwelling hydrodynamic-ecosystem (NPZ) model with an individual based model (IBM) for an intermediate sized (ca. 2.5 mm) copepod capable of diel vertical migration (DVM) at larger sizes. IBM simulations are done with different scenarios for behavioral responses; the interaction of the organisms with the circulation is evaluated by examining growth/development, reproduction, survival and distribution. Since ocean productivity in coastal upwelling systems is greatest nearshore, zooplankton production is favored by nearshore retention.
Our interests were in understanding how the responses of individuals to their environment could alter their behavior and influence nearshore retention and demographic processes. Below are flc format animations of individual distribtions and size (size of plotted symbol is related to size of individual) of two scenarios within an idealized 2D upwelling environment: 1) the individuals are passively advected and diffused only; and 2) the animals experience in the environment and its physiology influence their DVM behavior. Details are below. The table below provides links to selected jpg plots of the SEOM model results. A better way to visualize the results is using animated movies of the simulation. Larger images and FLC animations are available for viewing by clicking the images displayed below. Information about the FLC animation format and software for playing FLC animations is available at http://crusty.er.usgs.gov/flc.html. |
|
| run110 | run107 | Physical (SLICE) Model and Geometry Realistic Geometry found just North of Newport, OR Domain: 100 km in X; 200 m in Z 120 day simulation 10 days of upwelling favorable winds alternating with 10 days of no wind Output: U,V,W Velocities, Kv, Temperature, concentrations of dissolved inorganic nutrients, phytoplankton, and zooplankton (um N/L) |
Physical (SLICE) Model and Geometry SAME |
| POPCYCLE Individual Based Model Info Base Case Biology with No DVM |
POPCYCLE Individual Based Model Info Base Case Biology with DVM influenced by local vertical swimming speed influenced by:
|
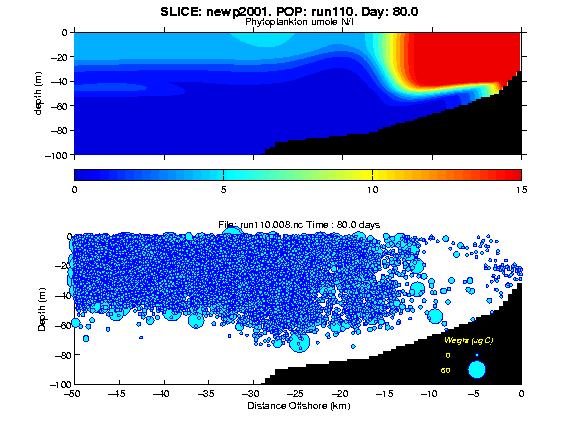
|
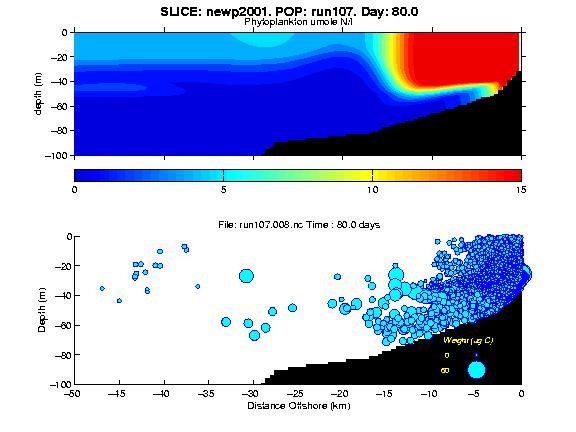
|