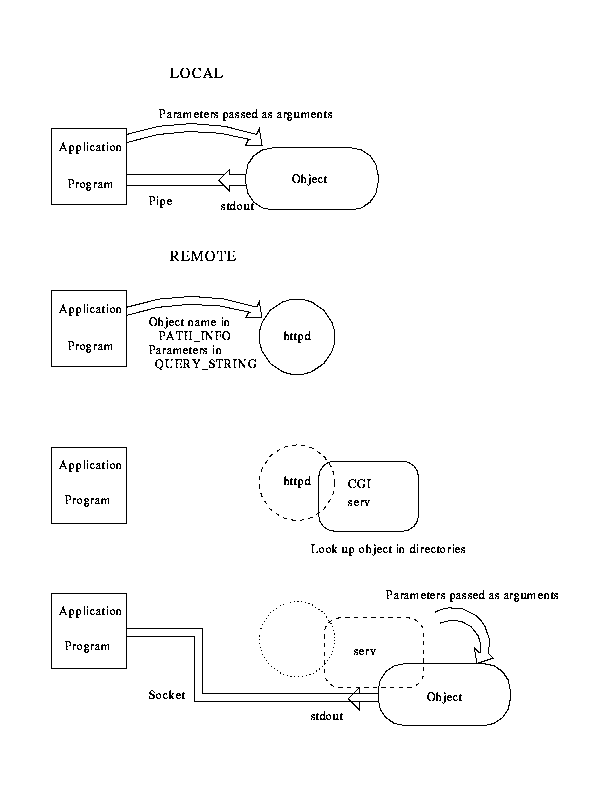
All exchanges between the user's application program (process 1) and the method/ translator (process 2 -- perhaps on another machine) are made via interprocess communications using ``pipes'' or ``sockets'' as defined in Berkeley UNIX. In the case of a locally defined object, a pipe is opened between the application and the method processes. For a remotely defined object, the application opens a socket to the HTTP daemon on the other machine and starts the server. The server effectively connects the standard output stream on the method to the socket in the application. The processes then begin exchanging information according to the JGOFS protocol.
